臨床検査において、L-グルタミンの測定に利用されます。
| 由来 | from microorganism |
|---|---|
| 系統名 | L-Glutamine amidohydrolase |
| EC 番号 | 3.5.1.2 |
| 反応式 | L-Glutamine + H2O →→→ L-Glutamineate + NH3 |

臨床検査において、L-グルタミンの測定に利用されます。
| 由来 | from microorganism |
|---|---|
| 系統名 | L-Glutamine amidohydrolase |
| EC 番号 | 3.5.1.2 |
| 反応式 | L-Glutamine + H2O →→→ L-Glutamineate + NH3 |
| Appearance | light gray lyophilizate | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity | ≧4 U/mg lyophilizate | |
| Contaminants | Catalase ≦3.0 U/U% | |
| Stabilizer | sucrose | |
| Storage condition | below - 20℃ |
| Molecular weight | ca. 58 kDa (gel filtration) |
|---|---|
| Structure | heterodimer (45 kDa and 22 kDa) (SDS-PAGE) |
| Michaelis constant | 5.5×10-4 M (L-glutamine) |
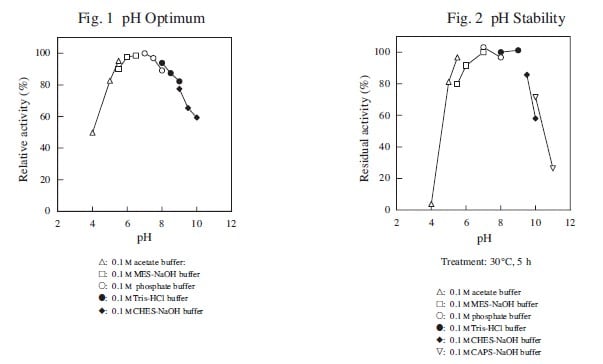
| pH Optimum | ca. 7.0 |
| pH Stability | 5.5–9.0 |
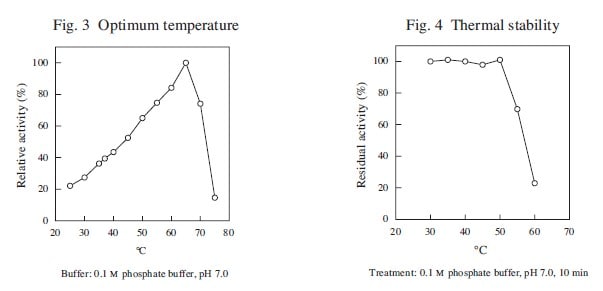
| Optimum temperature | ca. 65℃ |
| Thermal stability | below 50℃ |
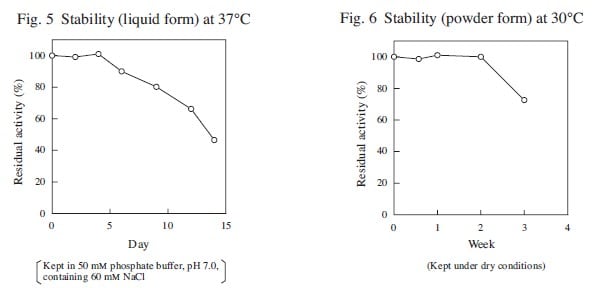
| Stability (liquid form) | stable at 37℃ for at least four days |
| Stability (powder form) | stable at 30℃ for at least two weeks |
| Specificity | L-glutamine (100), D-glutamine (70), L-asparagine (0), D-asparagine (0) |
The enzyme is useful for the determination of L-glutamine in clinical analysis.

The appearance of NADH is measured spectrophotometrically at 340 nm.
One unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme which produces 1 μmol of NADH per min at 37℃ and pH 6.0 under the conditions described below.
Sample: dissolve the lyophilized enzyme to a volume activity of 0.5–3.0 U/ml with ice-cold enzyme dilution buffer (Reagent I) immediately before measurement.
| 0.2 ml | L-Glutamine solution | (Reagent A) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.4 ml | Acetate buffer | (Reagent B) |
| 1.0 ml | Hydroxylamine buffer | (Reagent E) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 ml | NAD+ solution | (Reagent F) |
| 1.0 ml | Distilled water | |
| 0.05 ml | The supernatant of step 6 | |
| 0.025 ml | GLDH solution | (Reagent H) |
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula:
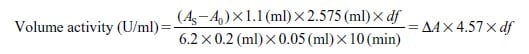
6.2 : Millimolar extinction coefficient of NADH at 340 nm (cm2/μmol)
df : Dilution factor
C : Content of glutaminase preparation in sample (mg/ml)
Roberts, E., “The Enzymes,” Vol. 4 (2nd ed.), Academic Press, New York and London, 1960, pp. 285–300.
Hartman, S. C., “The Enzymes,” Vol. 4 (3rd ed.), Academic Press, New York and London, 1971, pp. 79–100.