
マルトース及びキシロースに対する反応性が低いFAD依存性グルコース脱水素酵素です。血糖測定用酵素の中でも特に安定性に優れており、連続血糖測定センサに適しています。
| 由来 | recombinant A. sojae |
|---|---|
| 系統名 | D-Glucose : acceptor 1-oxidoreductase |
| EC 番号 | 1.1.5.9 |
| 反応式 | D-Glucose + acceptor →→→ D-Glucono-1,5-lactone + reduced acceptor |

マルトース及びキシロースに対する反応性が低いFAD依存性グルコース脱水素酵素です。血糖測定用酵素の中でも特に安定性に優れており、連続血糖測定センサに適しています。
| 由来 | recombinant A. sojae |
|---|---|
| 系統名 | D-Glucose : acceptor 1-oxidoreductase |
| EC 番号 | 1.1.5.9 |
| 反応式 | D-Glucose + acceptor →→→ D-Glucono-1,5-lactone + reduced acceptor |
| Appearance | yellow to brown lyophilizate |
|---|---|
| Activity | ≧700 U/mg lyophilizate |
| Contaminants | NAD glucose dehydrogenase <0.01 U/U% |
| Hexokinase <0.01 U/U% | |
| α-glucosidase <0.01 U/U% | |
| β-glucosidase <0.01 U/U% | |
| Storage condition | below -20℃ |
| Molecular weight | ca. 90 kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
|---|---|
| Structure | monomer, one mole of FAD per mole of enzyme glycoprotein |
| Michaelis constant | 6.4×10-2M (D-glucose) |
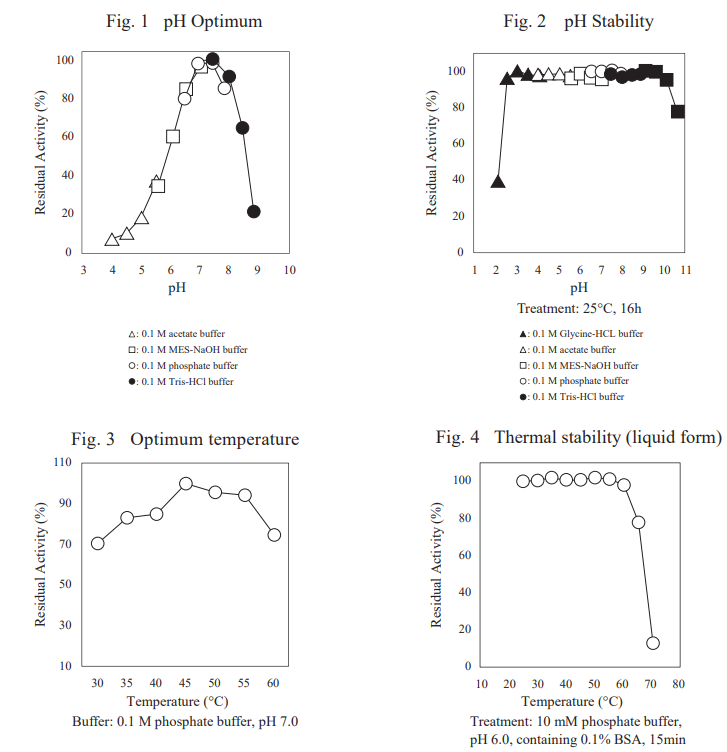
| pH Optimum | 7.0–7.5 (Fig.1) |
| pH Stability | 2.5–9.5 (Fig.2) |
| Optimum temperature | 45℃ (Fig.3) |
| Thermal stability (liquid form) | below 60℃ (Fig.4) |
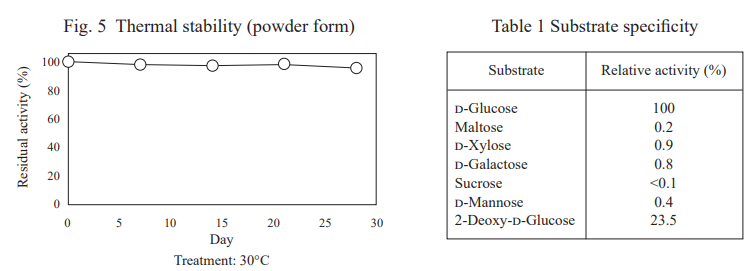
| Thermal stability (powder form) | stable at 30℃ for at least one month (Fig.5) |
| Inhibitors | Mn2+, Ag+ |
| Specificity (Table.1) | D-glucose (100%), maltose (0.2%), D-xylose (0.9%), D-galactose (0.8%) sucrose (<0.1%), D-mannose (0.4%) 2-deoxy-D-glucose (23.5%) |
FADGDH-ADと電子メディエータ修飾ポリマーを用いることで、グルコースを電極法により連続測定できます。
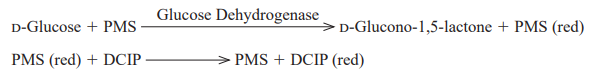
The disappearance of the blue color of DCIP by the reduction is measured spectrophotometrically at 600 nm.
One unit (U) causes the reduction of one micromole of DCIP per minute under the conditions described below.
Sample: dissolve the lyophilized enzyme to final concentration about 0.4 μg/mL with enzyme dilution buffer (Reagent E) immediately before measurement.
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula:
![]()
20.4 : Millimolar extinction coefficient of DCIP under the assay condition (cm2 /µmol)
1.0 : Light pass length (cm)
df : Dilution factor
Satake R, Ichiyanagi A, Ichikawa K, Hirokawa K, Araki Y, Yoshimura T, Gomi K (2015)
Novel glucose dehydrogenase from Mucor prainii: Purification,
characterization, molecular cloning and gene expression in Aspergillus sojae J. Biosci Bioeng., 120, 498-503
Masakari Y, Hara C, Araki Y, Gomi K, Ito K (2020)
Improvement in the thermal stability of Mucor prainii-derived FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase via protein chimerization Enzyme Microb Technol., 132, 109387